The human microbiome, a diverse community of microorganisms inhabiting the human body, has emerged as a key player in maintaining overall health. Dive into the history of microbiome research to understand its evolution and significance.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek’s Microscopic Observations (1670s)
In the late 17th century, Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek laid the foundation for microbiology with groundbreaking observations using a simple microscope.
Germ Theory and Pasteurization (1860s-1870s)
The 19th century witnessed the establishment of germ theory by Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch, linking microorganisms to infectious diseases and introducing pasteurization.
Antibiotics and Microbial Ecology (1920s-1960s)
The 20th century brought revolutionary discoveries like penicillin by Alexander Fleming, shaping medicine. Simultaneously, microbial ecology studies explored the diversity of microorganisms in different environments.
Advances in DNA Sequencing (Human Genome Project)
In the 1980s-1990s, the Human Genome Project marked a milestone, providing insights into the human genome and paving the way for comprehensive studies on the microbiome.
Human Microbiome Project (HMP) and Metagenomics (2000s)
The early 21st century witnessed the launch of the Human Microbiome Project, exploring microbial communities’ role in health. Metagenomics became a powerful tool in microbiome research.
Rise of Microbiome Research and Therapeutics (Mid-2010s)
Advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies expanded microbiome research, linking it to various health conditions like gastrointestinal disorders and metabolic diseases.
Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Applications (Present)
Ongoing research explores the intricate relationships between the microbiome and human health, with microbiome-based interventions like fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) at the forefront of precision medicine.
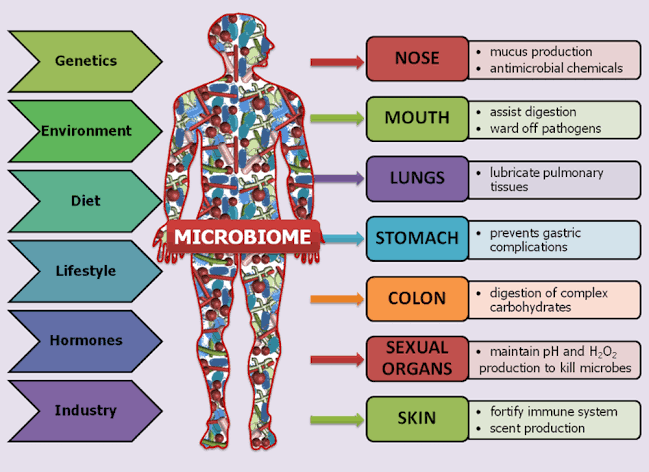
Unraveling the Microbiome’s Importance for Health
Understanding why the microbiome matters is crucial for overall well-being. Explore key reasons highlighting its significance:
Digestive Health
The gut microbiome aids in nutrient absorption and contributes to the breakdown of dietary fibers, promoting digestive health.
Immune System Support
A balanced and diverse microbiome plays a pivotal role in training and modulating the immune system, preventing inappropriate immune responses.
Protection Against Pathogens
A healthy microbiome acts as a barrier against harmful pathogens, contributing to the body’s defense mechanisms.
Metabolism and Energy Regulation
The gut microbiome influences nutrient metabolism and energy regulation, playing a role in maintaining a healthy weight.
Mood and Mental Health
The gut-brain axis is influenced by the microbiome, impacting mental health and conditions like anxiety and depression.
Vitamin Synthesis
Certain microbiome bacteria contribute to the synthesis of essential vitamins, supporting various physiological processes.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
A balanced microbiome helps regulate inflammation, crucial for preventing various health conditions.
Digestion of Dietary Fiber
Microbiome fermentation of dietary fiber produces short-chain fatty acids, contributing to gut barrier function and having anti-inflammatory properties.
Nurturing a Healthy Human Microbiome
Understanding the microbiome’s importance emphasizes the need to maintain a diverse and balanced microbial community. Lifestyle factors, including diet and stress, play a role in microbiome composition. Promote a healthy microbiome through a balanced diet, probiotics, and other lifestyle choices for overall well-being.





Leave a Reply